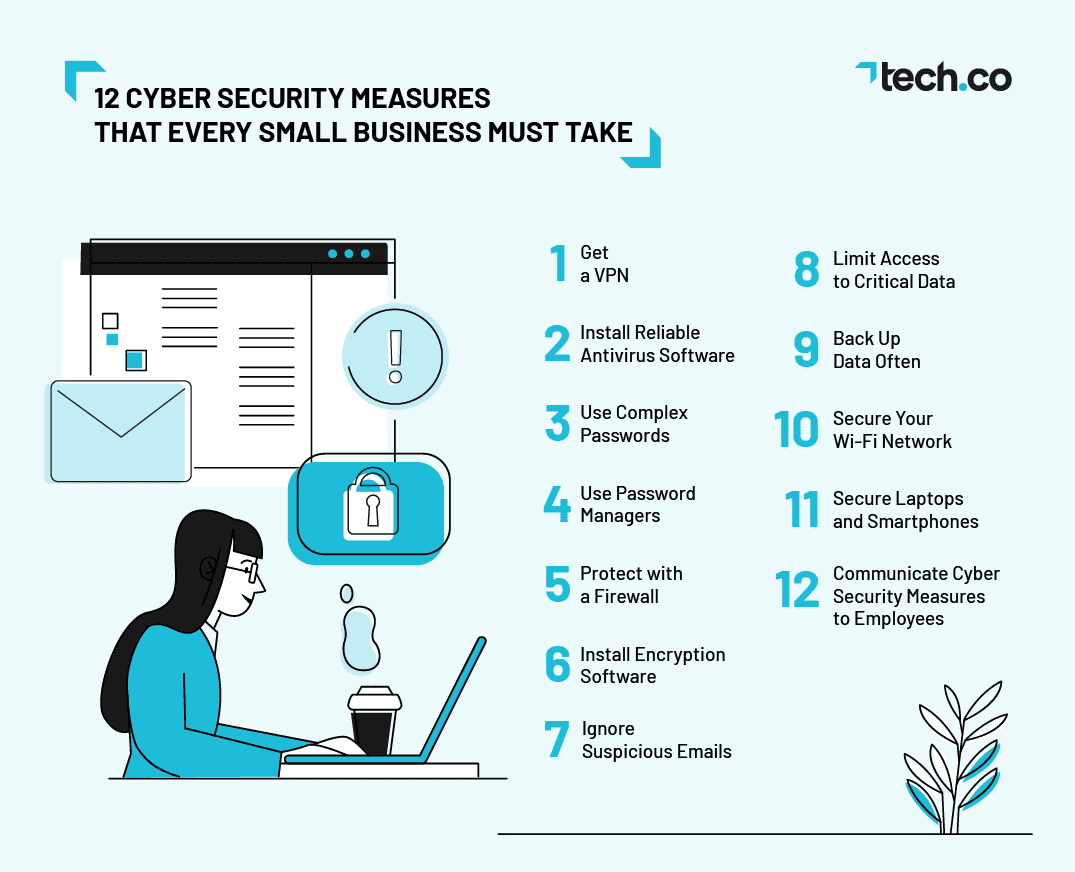
Small business owners and entrepreneurs need to be aware of the increasing threat of cyberattacks and data theft. Therefore, it is important to have a robust cybersecurity system in place. This article outlines ten crucial cybersecurity measures that every small business owner should take to ensure their networks, computer systems, and data are protected from cyberattacks. These measures include training employees on cybersecurity, securing networks with a firewall, using secure passwords and multifactor authentication, installing antivirus and anti-malware software, backing up data regularly, updating software and operating systems, restricting access to sensitive data, creating an incident response plan, monitoring systems regularly, and using virtual private networks for remote access. By implementing these measures, small businesses can reduce their risk of cyber threats and data breaches, build customer trust, and gain a competitive advantage in the digital landscape.
10 Cybersecurity Measures Every Small Business Should Take
In today’s digital age, data theft and security breaches are increasingly becoming a threat to all businesses. As a small business owner or entrepreneur, you must put in place a robust cybersecurity system to protect your company’s data, reputation, and investments. This article outlines ten crucial cybersecurity measures every small business should take to keep their networks, computer systems, and data safe from cybercriminals.
1. Train Your Staff on Cybersecurity
Training your staff on basic cybersecurity measures is fundamental. Teach them about cyber threats, how to identify them, how to respond to them, and best practices in password management. Your employees should also be aware of the techniques used by cybercriminals to infiltrate your business systems, such as phishing, malware, and ransomware.
2. Secure Your Network with a Firewall
A firewall is a software or hardware-based security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing traffic on your network. It acts as a barrier between your company’s internal systems and the internet, blocking unwanted traffic and unauthorized access to your network. Make sure to configure the firewall correctly, and keep it updated with the latest security patches and software updates.
3. Use Secure Passwords and Multifactor Authentication
Passwords should be complex, unique, and changed frequently. Encourage your staff to use a combination of lowercase and uppercase letters, numbers, and special characters in their passwords. Multifactor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring additional authentication factors, such as biometric identification, security tokens, or SMS codes, before granting access to company resources.
4. Install Antivirus and Anti-malware Software
Antivirus and anti-malware software protect your business from viruses, Trojans, and other malicious software that can harm your systems and steal sensitive data. These programs should be installed, configured, and updated regularly to ensure they are up-to-date with the latest security definitions.
5. Back Up Your Data Regularly
Data backup is critical for both disaster recovery and cybersecurity. Backing up your files and data regularly allows you to recover quickly from a cyber-attack or data breach. The backup files should be stored offsite or in the cloud, encrypted, and protected with access controls and strong passwords.
6. Update Software and Operating Systems Regularly
Regular software updates and patches can fix security bugs, add new features, and improve system performance. Cybercriminals often exploit unpatched vulnerabilities to infiltrate networks and steal data. Enable automatic updates for all software and operating systems, such as Windows, macOS, and Linux.
7. Restrict Access to Sensitive Data
Not all employees should have access to sensitive data, such as financial records, employee records, or customer data. Limit access to such data to only those who need it to perform their job functions. Enforce strong access controls, such as two-factor authentication and data encryption, to prevent unauthorized access.
8. Create an Incident Response Plan
An incident response plan is a documented, step-by-step approach to handling a security incident or data breach. It outlines the roles and responsibilities of everyone involved in the response, from first responders to management. The plan should be updated regularly and tested periodically to ensure it is effective.
9. Monitor Your Systems Regularly
Active monitoring of your network and systems can detect and respond to security threats quickly. Use intrusion detection and prevention systems, network traffic analysis, and security information and event management (SIEM) tools to detect unusual activity and suspicious behavior on your network.
10. Use Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) for Remote Access
Remote workers or telecommuters should use VPNs for secure access to company resources. A VPN creates an encrypted connection between the remote worker’s device and the company’s network, preventing third-party access to sensitive data. VPNs are also useful for accessing public Wi-Fi networks, which are often insecure and prone to cyber threats.
In conclusion, implementing these ten cybersecurity measures can significantly reduce your small business’s risk of cyber threats and data breaches. Be proactive in your security approach and invest in the necessary tools and resources to protect your company’s data and reputation. Good cybersecurity practices not only protect your business, but they also build customer trust and provide a competitive advantage in today’s digital landscape.